

Last Updated: 06 October, 2024 5 Mins Read
A search algorithm is a procedure used to find a specific element within a collection of elements, such as an array, list, tree, graph, or database. The goal of a search algorithm is to determine whether a specific element exists in the data structure and, if so, to find its position or retrieve it.
Search algorithms are fundamental in computer science and are used in a wide range of applications, including data retrieval, artificial intelligence, optimization, and more.
In this tutorial, we are going to exlore how to search for a specific element within a collection of elements using a binary search algorithm in Java.
The binary search algorithm is a technique for searching a specific element within a sorted list of elements. It uses the divide-and-conquer approach to rapidly find the specific element by repeatedly dividing the search space in half.
If the specific element is less than the middle element, it can't be in the right half of the data structure, so discard it and focus on the left half. Conversely, if the target element is greater, discard the left half and focus on the right half and continue this process of dividing and searching until we either find the target element or reach an empty sub-array, indicating the element is not present.
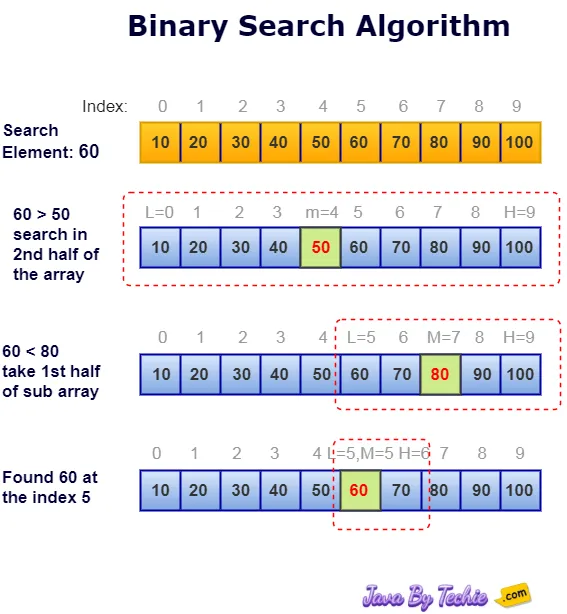
The binary search algorithm is powerful and efficient. It is achieving a time complexity of O(log n), where n is the total number of elements in the list. It is significantly faster than linear search (O(n)).
There are the following ways to implement binary search in Java:
Here is an example of a binary search using the iterative approach in Java.
Output
Element 40 is present at the index 3
Element 250 is not present in array
Output
Element 40 is present at the index 3
Element 250 is not present in array
In Java, the java.util.Arrays.binarySearch() method is a utility provided to perform a binary search on the sorted arrays. It is a very simple and highly efficient way to search for an element.
Here is an example of a binary search using the Arrays.binarySearch() method.
Output
The key: 60 found at the index = 5
The key: 100 is not found in the array
Time complexity: The time complexity of Arrays.binarySearch() is O(log n), where n is the size of the array.
Java has provided another utility method to search an element from the sorted list of elements that is java.util.Collections.binarySearch(). This utility method is similar to Arrays.binarySearch() but is works with List implementations such ArrayList, LinkedList, etc.
Here is an example of a binary search using the Collections.binarySearch() method.
Output
The key: 30 found at the index = 2
The key: 90 is not found in the list
Time complexity: The time complexity of Arrays.binarySearch() is O(log n), where n is the size of the list.
That's all, guys. I hope this article is helpful for you.
Happy Learning... 😀
feedback@javabytechie.com