

Last Updated: 26 August, 2023
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is based on four core concepts: abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
In this article, we are going to discuss all about encapsulation in Java with examples.
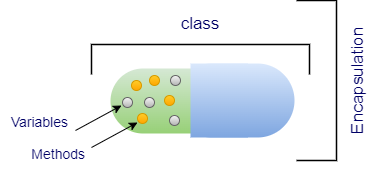
Encapsulation is the mechanism of wrapping data (variables) and behavior (methods) together in a single unit (class).
The data of an encapsulated class will be hidden from other classes and cannot be accessed directly outside of it. It can only be accessed outside of the class through the public methods of its current class. Encapsulation helps achieve data hiding in Java.
An example of a fully encapsulated class is the Java Bean class.
Declare the variables of a class as private.
Other classes cannot directly access private variables.
Provide public setter and getter methods.
Using these public methods, private variables can be accessed or modified outside of the class.
Here's a simple example of encapsulation in Java:
Class: AccountDetails.java
In this AccountDetails class, the attributes customer_name, account_number, and balance are encapsulated by making them private. Public getter and setter methods are provided to access and modify these attributes outside the class.
Class: EncapsulationExample.java
Output
Submitted Documents :
Aadhar Card and PAN Card
Customer Name : John
Account Number : 123456789
Account Balance : 500000.0
In the EncapsulationExample class, creating the object of the AccountDetails class, using the setter methods to set the values of the attributes of the AccountDetails class, and accessing the attributes using the getter methods.
By using encapsulation, we ensure that the internal representation of our class remains hidden from external manipulation, and we can control how data is accessed and modified, leading to more maintainable and robust code.
That's all guys, hope this Java article is helpful for you.
Happy Learning... 😀
feedback@javabytechie.comWhat is encapsulation in Java?
Encapsulation is the mechanism of wrapping data (variables) and behavior (methods) together in a single unit (class). The data of an encapsulated class will be hidden from other classes and cannot be accessed directly outside of it. It can only be accessed outside of the class through the public methods of its current class. Encapsulation helps achieve data hiding in Java.
How do we achieve 100% data encapsulation in Java?
Ans. In order to achieve 100% data encapsulation in Java, we need to follow the below points:
Abstraction vs Encapsulation in Java
Ans. Abstraction and encapsulation are both core concepts of object-oriented programming. They are different from each other in terms of features and implementation in Java.
Encapsulation and data hiding are both the same in Java?
Ans. No, data hiding means protecting the variables of a class from outside access, whereas encapsulation means wrapping or binding data into a single unit.
What is a "tightly encapsulated class" in Java?
A class is said to be tightly encapsulated if and only if all the data members (variables) of that class are declared private. If a class has all variables declared as private, and if it's inherited by another class that too has all private data members, then the later one is also said to be a tightly encapsulated class.
How to achieve data hiding in Java programming?
By declaring data members (variables) as private, we can achieve or implement data hiding in Java. Private properties of a class cannot be accessed directly outside of the class.
The main advantage of hiding data is that we can achieve security.
Does reflection violate encapsulation in Java?
Reflection violates encapsulation because it reveals the internal data structures.
Explain a design pattern based on encapsulation in Java?
Ans. Encapsulation is a technique that Java uses in multiple design patterns, including the factory pattern, which generates objects.
For constructing the objects of those classes whose creation logic may vary, the factory design is a preferable option. Additionally, it is employed in the development of various interface implementations.
The JDK's BorderFactory class, which generates various border types and wraps the border generation code, is a nice illustration of encapsulation in Java.
What are the advantages of encapsulation in Java?
Please refer to the Tutorial Tab on the same page.
How do getter and setter methods help in encapsulation?
In encapsulation, all the private attributes are accessed or modified from the outside class using the getter and setter methods. All these getter and setter methods are declared public access modifiers.